55 Degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit: Easy Conversion Guide
Temperature conversion can be confusing if you’re not familiar with the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. Many people struggle to grasp how hot or cold a specific Celsius reading feels in Fahrenheit. One commonly asked question is about 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit. What does it really mean? How hot is that in everyday terms? And where might you encounter such a temperature?
In this guide, we’ll break down 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit, explain the conversion process, explore practical examples, and give insights into why knowing this conversion matters in real life. Whether you’re cooking, studying weather, or handling industrial processes, this guide will make the numbers easy to understand.
Understanding the Basics: Celsius vs. Fahrenheit
Before diving into 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit, it helps to understand the two temperature scales:
- Celsius (°C): Used globally, especially in science and most countries outside the U.S. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C.
- Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the United States. Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F.
The scales differ in their starting points and increments. Celsius divides the freezing and boiling points of water into 100 equal parts, while Fahrenheit divides it into 180 parts.
2: Why Temperature Conversion Matters
Understanding conversions is more than just a math exercise. There are several real-life scenarios where knowing 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit is important:
- Cooking and Baking: Oven temperatures are often listed in Fahrenheit in the U.S. while recipes from other countries use Celsius.
- Weather Awareness: Extreme heat events can be alarming without accurate understanding. 55°C is exceptionally hot and can have serious implications.
- Industrial Processes: Certain machinery and chemical reactions require precise temperature control, making conversion vital.
- Science Experiments: Students and researchers must often convert temperatures between systems to compare results accurately.
How to Convert 55 Degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit
The formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit is simple:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Applying this formula for 55 degrees Celsius:
-
Multiply 55 by 9/5:
55 × 9/5 = 99 -
Add 32:
99 + 32 = 131°F
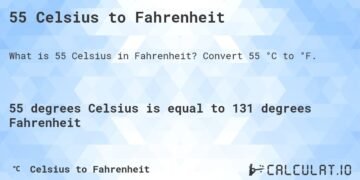
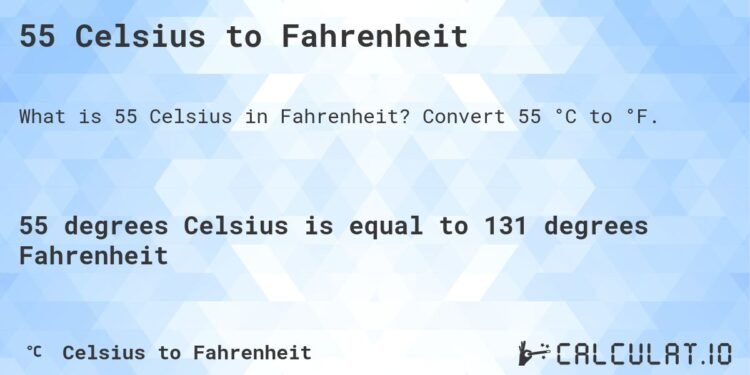
So, 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit equals 131°F.
This result gives you a tangible sense of how hot 55°C is. Most people don’t feel comfortable in temperatures above 40°C, so 55°C (131°F) is extremely hot by any standard.
H3: Quick Reference Table
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|
| 50 | 122 |
| 55 | 131 |
| 60 | 140 |
| 65 | 149 |
| 70 | 158 |
This table provides a quick visual for common high-temperature conversions, showing how 55°C compares to other extreme temperatures.
Real-Life Examples of 55 Degrees Celsius
Understanding numbers is easier when you have context. Here’s where you might encounter 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit (131°F):
3: Weather Extremes
Some of the hottest places on Earth, like Death Valley in California or parts of the Middle East, have recorded temperatures nearing 55°C. Such heat is dangerous for humans, requiring precautions like hydration, shade, and protective clothing.
3: Industrial Applications
In industries, 55°C is a common target temperature for processes such as:
- Pasteurization of liquids
- Heating solutions in chemical reactions
- Material testing in engineering labs
3: Cooking and Food Preparation
Certain ovens or food preparation processes may reach around 55°C for slow-cooking or warming, particularly in professional kitchens or sous-vide cooking, where precise temperature control is critical.
3: Household Appliances
Water heaters, saunas, and steam baths often operate near 55°C, highlighting why it’s important to know the Fahrenheit equivalent, especially for safety.
Understanding the Feeling of 55 Degrees Celsius
For humans, 55°C (131°F) is extremely uncomfortable. Extended exposure can lead to:
- Heat exhaustion
- Dehydration
- Heatstroke
Even short-term contact with water at this temperature can cause burns. That’s why temperature awareness in both Celsius and Fahrenheit is crucial for safety.
3: Comparing With Other Temperature Benchmarks
- Human body temperature: ~37°C (98.6°F)
- Boiling point of water: 100°C (212°F)
- Saunas: 70–100°C (158–212°F)
- 55°C = hot water temperature, potentially dangerous for prolonged exposure
Tips for Converting Temperatures Quickly
If you frequently need to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit:
- Remember the formula: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
- Use approximations for rough estimates:
- °C × 2 + 30 ≈ °F (good for quick mental math)
- Keep a conversion table handy for extreme temperatures like 55°C
- Use digital thermometers that switch between °C and °F for convenience
4: Mental Trick
For temperatures above 50°C, add 100 to the Celsius value and add about 30. For example:
55 + 100 = 155 → roughly 131°F after adjustments
Why 55 Degrees Celsius Is Significant
- Extreme heat can be dangerous for humans, animals, and even electronics.
- It marks the upper threshold for many outdoor activities in hot climates.
- Industries often use this temperature for precise processes, highlighting its practical importance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How hot is 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit?
55°C equals 131°F, which is extremely hot and can cause burns or heat exhaustion.
Is 55 degrees Celsius dangerous?
Yes, direct human exposure can be dangerous without protection or hydration.
How do I convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
Use the formula °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32 for accurate conversion.
Can I encounter 55°C in everyday life?
Yes, in saunas, water heaters, industrial processes, or extreme weather conditions.
Practical Applications of Knowing This Conversion
Understanding 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit helps in:
- Kitchen safety when cooking or warming food
- Outdoor safety in extreme climates
- Industrial settings where precise heating is required
- Science and education for accurate reporting
4: Safety Tips
- Avoid prolonged exposure to hot surfaces or water at 55°C
- Use protective gear in industrial or cooking environments
- Hydrate adequately in hot climates
- Monitor children and pets closely in extreme temperatures
Conclusion
Knowing 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit is more than just a math exercise. It helps you understand heat levels in practical, everyday terms—whether you’re cooking, working in industrial settings, or navigating extreme weather. 55°C converts to 131°F, signaling an extremely hot temperature that requires caution for safety.
By understanding this conversion, you can make smarter decisions in daily life, protect yourself from heat-related risks, and communicate temperatures accurately in any environment. Keeping a mental or physical conversion reference ensures you’re always prepared when Celsius and Fahrenheit numbers appear.
Understanding 55 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit bridges the gap between two measurement systems, making the world of temperature clearer, safer, and more manageable.