How to Make a Sales Return Journal Entry Correctly
Accounting can feel overwhelming, especially when dealing with returns, adjustments, and corrections. One of the most commonly misunderstood transactions is the Sales Return Journal Entry. Whether you’re a student, a small business owner, or a professional accountant, knowing how to record sales returns correctly is essential to maintain accurate financial records, prevent discrepancies, and keep your accounts balanced.
In this guide, we’ll explore the concept of a Sales Return Journal Entry, its importance, step-by-step instructions for recording it, practical examples, common mistakes to avoid, and best practices to streamline accounting processes.
By the end of this article, you’ll not only understand how to make a Sales Return Journal Entry, but you’ll also see why it is a critical part of business accounting.
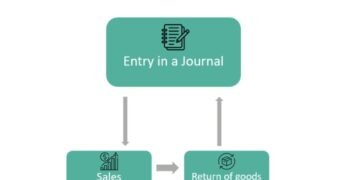
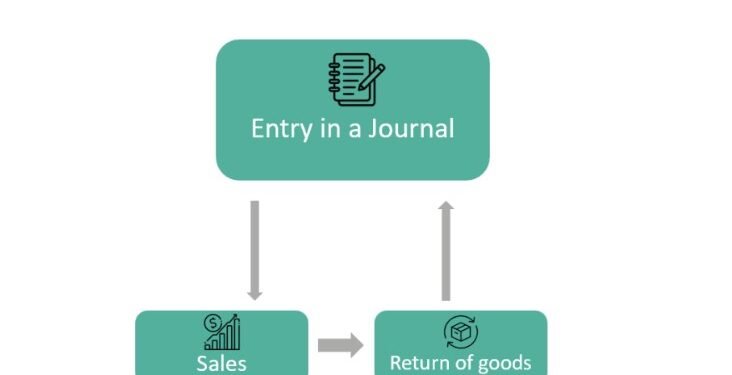
What Is a Sales Return Journal Entry?
A Sales Return Journal Entry is a record of goods returned by a customer. Unlike regular sales, these entries reduce the revenue of a business and adjust accounts receivable. Essentially, it’s the accounting treatment for returned products and ensures that financial statements reflect the correct net sales.
Key Features:
- Initiated when customers return sold goods.
- Reduces sales revenue.
- Affects accounts receivable if payment was on credit.
- Recorded in a Sales Return Journal before posting to the general ledger.
Understanding the purpose of a Sales Return Journal Entry helps in maintaining transparent accounting practices and accurate financial reporting.
Importance of Recording Sales Returns
Properly recording a Sales Return Journal Entry is vital for multiple reasons:
- Accurate Revenue Reporting: Ensures net sales reflect only goods retained by customers.
- Inventory Accuracy: Returns affect stock levels and must be reflected in inventory records.
- Cash Flow Management: Helps track refunds or adjustments for credit sales.
- Audit Compliance: Provides proof for auditors that returns are correctly recorded.
- Customer Accountability: Shows professional handling of returns and disputes.
Failing to record sales returns can lead to inflated revenue, inventory mismatches, and potential errors during audits.
Step-by-Step Guide to Making a Sales Return Journal Entry
Recording a Sales Return Journal Entry is straightforward once you understand the process.
Step 1: Identify the Returned Goods
- Verify the quantity and condition of returned items.
- Confirm the original invoice or sales transaction.
Step 2: Determine the Financial Impact
- For cash sales, record a reduction in cash or refund issued.
- For credit sales, adjust accounts receivable.
Step 3: Prepare the Journal Entry
The typical journal entry for a sales return is:
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| xx/xx/20xx | Sales Return A/C | 500 | |
| To Accounts Receivable A/C | 500 |
Explanation: This entry decreases sales revenue and reduces the amount receivable from the customer.
Step 4: Post to Ledger Accounts
- Update the Sales Return account.
- Adjust the Accounts Receivable account.
Step 5: Update Inventory Records
- Return goods to inventory if resalable.
- Adjust stock levels in the inventory system.
Examples of Sales Return Journal Entries
Let’s explore some practical scenarios to understand the process better:
Example 1: Credit Sale Return
ABC Traders sold $1,000 of office supplies on credit. The customer returned $200 worth of damaged items.
Journal Entry:
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Return A/C | 200 | |
| To Accounts Receivable A/C | 200 |
Outcome: Revenue decreases by $200, and the customer’s outstanding balance is adjusted.
Example 2: Cash Sale Return
XYZ Ltd. sold goods for $500 in cash. $50 worth of items were returned.
Journal Entry:
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Return A/C | 50 | |
| To Cash A/C | 50 |
Outcome: Cash balance decreases, and net sales are adjusted.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced accountants sometimes make mistakes while recording sales returns. Here are the common ones:
- Not verifying the original invoice before recording the return.
- Recording the return in the wrong period, affecting financial statements.
- Ignoring inventory adjustments, causing stock mismatches.
- Failing to update accounts receivable or cash accounts for accurate balances.
- Double-counting returns, leading to understated revenue.
Avoiding these errors ensures smooth accounting and reliable financial records.
Best Practices for Handling Sales Returns
Efficient management of Sales Return Journal Entries can save time, prevent errors, and improve customer satisfaction.
Tips:
- Maintain a dedicated sales return register.
- Cross-check returns against original invoices.
- Train staff to inspect returned goods carefully.
- Use automated accounting software for accurate posting.
- Review returns periodically to identify trends or recurring issues.
By following these best practices, businesses can streamline their accounting processes and maintain accurate records.
Impact of Sales Returns on Financial Statements
Recording a Sales Return Journal Entry directly affects multiple financial reports:
- Income Statement: Reduces net sales, impacting gross profit.
- Balance Sheet: Adjusts accounts receivable or cash balances.
- Inventory Records: Reflects returned stock accurately.
- Cash Flow Statement: Shows cash refunds for returned goods.
Accurate entries ensure all stakeholders have a true picture of the company’s financial position.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Does a Sales Return affect profit?
Yes, because it reduces net sales, which impacts gross and net profit.
Q2: Is a Sales Return Journal Entry mandatory?
While not legally mandatory, it’s essential for accurate accounting and audit compliance.
Q3: How do cash and credit returns differ?
Cash returns adjust the cash account, while credit returns adjust accounts receivable.
Key Takeaways
- Sales Return Journal Entry records returned goods, affecting revenue and accounts receivable.
- Always verify invoices and the condition of returned goods.
- Use proper ledger accounts to maintain accuracy.
- Regularly review entries to prevent errors and audit issues.
- Integrate inventory updates for complete financial accuracy.
Conclusion
Mastering the Sales Return Journal Entry is crucial for maintaining precise financial records and ensuring transparency in business operations. By following the steps, examples, and best practices outlined above, accountants and business owners can avoid errors, improve reporting accuracy, and strengthen trust with customers and auditors alike.
Whether dealing with cash or credit sales, understanding how to make a Sales Return Journal Entry correctly will enhance your accounting workflow and give you a clearer view of your business’s financial health.